The process of analyzing big data within big organizations can be complicated. There can be many data sets to analyze, some which are stored in silos or contain secure information. And there can be many different Hadoop users accessing these data sets, each with different permissions and credentials. So how can organizations effectively manage multiple data sets and Hadoop users?
In EMC® Isilon® OneFS®, you can take advantage of multitenancy to tackle this issue. Multitenancy creates secure, separate namespaces on a shared infrastructure so that different Hadoop users (or tenants) can connect to an Isilon cluster, run Hadoop jobs concurrently, and consolidate their Hadoop workflows onto a single cluster. OneFS 7.2 supports several Hadoop distributions and HDFS 2.2, 2.3, and 2.4. The OneFS HDFS implementation also works with Ambari for management and monitoring, Kerberos authentication, and Kerberos impersonation.
The white paper, “EMC Isilon Multitenancy for Hadoop Big Data Analytics,” highlights how to set up access zones for multitenancy and manage Hadoop data in an Isilon cluster.
How Hadoop works in Isilon
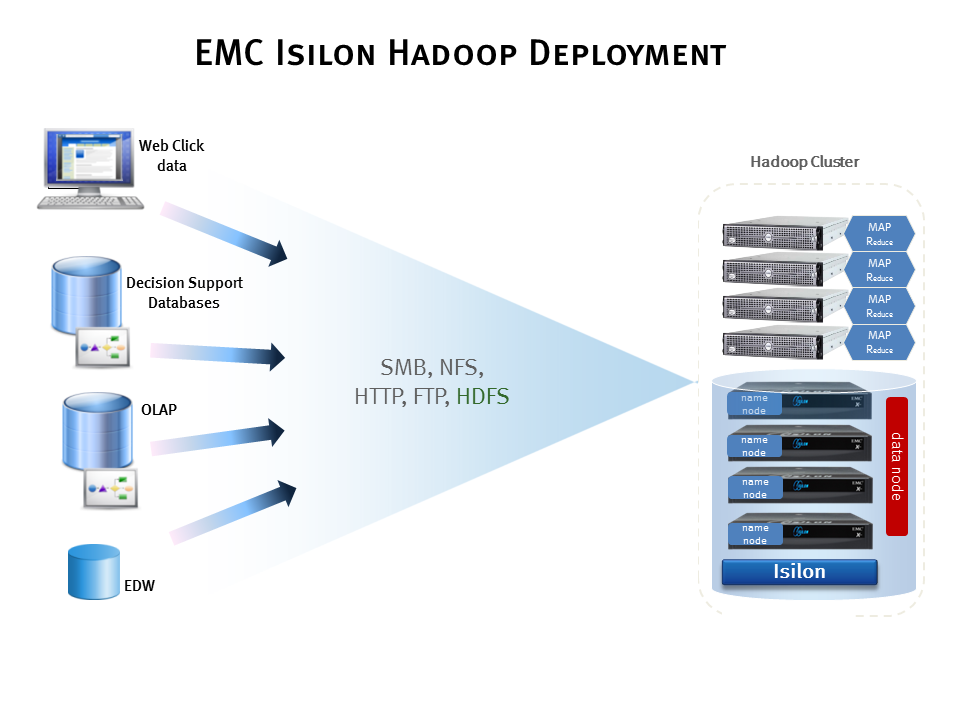
The Apache Hadoop analytics platform comprises the Hadoop Distributed File System, or HDFS, a storage system for vast amount of data, and MapReduce, a processing paradigm for data-intensive computation analysis.
EMC Isilon serves as the file system for Hadoop clients. This enables Hadoop clients to directly access their datasets on the Isilon storage system and run data analysis jobs on their compute clients. OneFS implements server-side operations of the HDFS protocol on each node in the Isilon cluster to handle calls to the NameNode and to manage read/write requests to DataNodes.
To configure an Isilon cluster for Hadoop, you first need to activate a HDFS license in OneFS. Contact your account team for more information. Then visit our EMC Hadoop Starter Kits to learn how to deploy multiple Hadoop distributions, such as Pivotal, Cloudera, or HortonWorks, on your Isilon cluster.
Access zones for multitenancy
Access zones lay the foundation for multitenancy in OneFS. Access zones provide a virtual security context that segregates tenants and creates a virtual region that isolates data sets. Each access zone encapsulates a namespace, HDFS directory, directory services, authentication, and auditing. An access zone also isolates system connections for further security.
The following procedures for managing and securing data sets are covered in “EMC Isilon Multitenancy for Hadoop Big Data Analytics.”
- Provide multiprotocol support – Learn how you can store data by using existing workflows on your Isilon cluster and access it through SMB, NFS, OpenStack Swift, and HDFS protocols, instead of running HDFS copy operations to move data to Hadoop clients.
- Manage different data sets – Learn how you can use SmartPools for managing different data sets based on customized policies.
- Associate network resources with access zones – Understand how virtual racking works in Isilon and how you can configure SmartConnect in OneFS to manage connections to data on your Isilon cluster.
- Secure access zones – Review how role-based access control and directory services with access zones in OneFS are used to authenticate users assigned to each zone.
Hadoop information hubs
You can find a rich array of information about Isilon and Hadoop. Visit our online Isilon Community on the EMC Community Network for InfoHubs, which serves as a single location for all of our Hadoop-related content. The Hadoop InfoHub contains links to general information about Isilon and Hadoop. The Cloudera with Isilon InfoHub contains links to information about deploying the Cloudera distribution for Isilon.
Start a conversation about Isilon content
Have a question or feedback about Isilon content? Visit the online EMC Isilon Community to start a discussion. If you have questions or feedback about this blog, contact us at isi.knowledge@emc.com. To provide documentation feedback or request new content, contact isicontent@emc.com.